- India
- International
UPSC Key | Forest fires, Pulitzer honours, Child labour and more
Exclusive for Subscribers from Monday to Friday: How are Forest fires and Child labour relevant to the UPSC Exam? What significance do topics like Pulitzer honours and Unemployment have for the preliminary and main exams? You can learn more by reading the Indian Express UPSC Key for May 8, 2024.
 The forest fire season in India lasts between November to June. Several factors like temperatures, precipitation, vegetation, and moisture contribute to the scale and frequency of these fires. Know more in our UPSC Key.
The forest fire season in India lasts between November to June. Several factors like temperatures, precipitation, vegetation, and moisture contribute to the scale and frequency of these fires. Know more in our UPSC Key.Important topics and their relevance in UPSC CSE exam for May 8, 2024. If you missed the May 7th, 2024 UPSC CSE exam key from the Indian Express, read it here.
🚨 The Indian Express UPSC Essentials brings to you the April edition of its monthly magazine. Click Here to read. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com🚨
The Editorial Page
Blaze in hills
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Environment
Mains Examination: GS-III: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
What’s the ongoing story- At least five people have lost their lives in the fires that have now spread over 1,000 hectares of forests in much of Uttarakhand. There is a danger of the blaze fanning out to heavily populated urban centres including Nainital city. Poor visibility has constrained the Air Force’s firefighting efforts.
Prerequisites:
— What is the blaze?
— What is climate crisis?
Key takeaways:
— Experts believe that burning forests intensifies heat and leads to black carbon emissions, adversely affecting water systems and air quality.

— Forest fires are, however, a far too serious problem to be doused by bans and punitive measures. The gutting of Uttarakhand’s forests is a sign of the aggravating climate crisis.
— Nearly 95 percent of forest fires in the country, including in Uttarakhand, are initiated by human activities. Historically, the accumulation of pine needles on the forest floor during the summer months was the main reason for the fires in the Himalayan season.
— Some of the combustion is necessary for the forest to regenerate — the burning of litter promotes the growth of fresh grasses.
— The monsoon was deficient in large parts of the state last year… Uttarakhand has witnessed its driest April in five years. In such moisture-deficient conditions, fire spreads fast, especially in oxygen-rich environs such as forests.
— The Himalayan state’s forest department has initiated remedial measures like putting in place firelines — gaps in vegetation to check the spread of the blaze.
— Uttarakhand’s forests need more proactive measures including putting in place weather prediction systems, satellite monitoring and training communities to become first responders.
For Your Information:
— According to experts, three factors cause the spread of forest fires — fuel load, oxygen and temperature. Dry leaves are fuel for forest fires. The Forest Survey of India (FSI) website states that nearly 36 per cent of India’s forests are prone to frequent fires.
— The FSI website adds: “Severe fires occur in many forest types particularly dry deciduous forest, while evergreen, semi-evergreen and montane temperate forests are comparatively less prone (India State of Forest Report 2015)… Nearly 4% of the country’s forest cover is extremely prone to fire, whereas 6% of forest cover is found to be very highly fire prone (ISFR 2019).”
Points to Ponder:
— What is bumbi bucket?
— How common are forest fires in India?
— What initiatives have been taken by the government to mitigate forest fires?
Post Read Question:
Prelims
Consider the following: (2019)
1. Carbon monoxide
2. Methane
3. Ozone
4. Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into the atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Mains
How far Anthropogenic activities are responsible for forest fires? What necessary steps need to be taken to avoid this?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Uttarakhand forest fire: How are forest fires caused and how frequent are they in India?
Unemployment vs wages
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Economic and Social Development
Mains Examination: GS-II, GS-III: Government Policies and intervention, Employment, human resources
What’s the ongoing story- Manish Sabharwal writes: “Recent rhetoric that Pakistan’s unemployment is lower than India’s, 300 million people have withdrawn from India’s labour force, and youth unemployment is at 45 per cent validates Nobel laureate Angus Deaton’s suggestion that “the pronouncements of economists can now be predicted by their politics”. The only real data in labour markets — everything else is a model — are prices and votes.”
Prerequisites:
— What are fiscal and monetary policy?
— What are redistributive and contributive justice?
— What is the unemployment rate?
Key takeaways:
— “The noise around unemployment arises from the CMIE Consumer Pyramids Household survey. The “is India broken” worldview of Ashoka Mody, that 300 million workers have withdrawn in frustration, ignores high-wage employers’ inability to fill open roles despite lower hiring standards.”
— “ Our low 4-8 per cent unemployment rate since 1947 is not a fudge; the poor cannot afford to be unemployed, so they self-exploit in subsistence agriculture… This suggests our problem isn’t unemployment but wages.”
— “This diagnosis matters because fiscal and monetary policy is the three-pronged world of emergency medicine; it treats the patient, not the disease.”
— “Thankfully, the last decade found the policy Madhyam Marg… (i) First, an efficiency, effectiveness, and technology revamp of India’s welfare state targeting our bhooka, beghar and beemar financed by higher tax collections so public debt and inflation stayed under control.
(ii) The non-profit digital public infrastructure that harnessed private innovation for identity, financial inclusion, and e-commerce.
(iii) Raising private employer productivity through formalisation (moving from deals to rules), PLI, NEP, GST, IBC, MPC, FDI, roads, airports, apprentices, decriminalisation, etc.
— “The latest ASER report and GERs suggest more kids are in school and college and have more years of education than ever before. Investor confidence… suggests traditional job creation constraints like infrastructure, skills and regulatory cholesterol are shifting from being a dagger in the heart to a thorn in the flesh.”
— “Over the last 10 years, our annual salary primer details how Rs 18,000 and 28,000 per month have become the base and average for the fastest-growing segment of bottom-of-pyramid jobs in 5,000 plus pin codes: Sales, customer service and logistics.”
— “Finally, elections provide the most critical information about labour markets because it is patronising to believe that massive national unemployment will not manifest itself in our fearless voting and fair counting.”
For Your Information:
— India Employment Report 2024, highlights some major positive developments in the labour market.
(i) The employment quality, as shown by a robust Employment Condition Index, has improved in all states.
(ii) There is an increase in the share of non-farm employment (and a decline in agriculture employment) between 2000 and 2019…
Points to Ponder:
— How is unemployment measured in India?
— How does India benefit from demographic dividends?
— What are the Government’s Initiatives Related to Employment?
(Thought Process: Understand the reason for unemployment in India–Mention about MGNREGA, Start-Up India, Rozgaar Mela, PMKVY–Significance of skill development for India to utilise demographic dividends.)
Post Read Question:
Prelims
Disguised unemployment generally means (2013)
(a) Large number of people remain unemployed
(b) Alternative employment is not available
(c) Marginal productivity of labour is zero
(d) Productivity of workers is low
Mains
Most of the unemployment in India is structural in nature. Examine the methodology adopted to compute unemployment in the country and suggest improvements. (2023)
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Why youth unemployment is India’s biggest challenge
Beyond the semantics
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Social Development – Inclusion, Social Sector Initiatives, etc
Mains Examination: GS-II: Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions, and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
What’s the ongoing story- In a sign of progressive intent, a three-judge Supreme Court (SC) bench, comprising Chief Justice D Y Chandrachud and Justices J B Pardiwala and Manoj Misra extended the ambit of pregnancy to include non-binary people and transgender men, among other gender identities, in addition to cisgender women.
Prerequisites:
— Who constitutes the LGBTQIA+ communities?
— What are the constitutional provisions related to equality?
— Know about the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act.
Key takeaways:
— In its ruling in A (Mother of X) v. State of Maharashtra, involving the termination of pregnancy of a 14-year-old girl, the judges used the term “pregnant person/(s)” over 40 times, clarifying in a footnote that their reason for doing so was an acknowledgement of a wider, more inclusive gender spectrum. In a country where gender rights, including, especially, LGBTQIA+ rights, has had a chequered trajectory, this is a welcome, necessary step.
— The SC’s nod comes as an expansion of its ongoing efforts to sensitise the legal fraternity — and by extension, the people of the land — to the nuances of neutral language.
— In broadening categories of identity, this shift in language goes beyond semantics. It urges a reimagination of gender and intersectionality that is not limited to binaries and that recognises the agency of individuals. The Court’s acknowledgment represents a vital step towards recognising legal protections for everyone capable of experiencing pregnancy.
— It is also in keeping with the language of its judgment on same-sex marriage last year in which it urged for legislative safeguards for same-sex couples.
Points to Ponder:
— Why gender-neutral language is important for making an inclusive society?
— What are the challenges faced by the LGBTQIA+ community in India?
— What are some of the Important SC’s Judgments related to the Rights of Sexual Minorities?
— What changes can be made at grassroots level for gender sensitisation?
— What is Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code?
Post Read Question:
Which of the following is a fundamental right?
(a) Right to information
(b) Right to marry
(c) Right to property
(d) Right to education
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
The Ideas Page
Playing the field
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: GS-II: International Relations
What’s the ongoing story- C Raja Mohan writes: Xi Jinping’s swing through Europe this week highlights China’s bold play to exploit the divisions within Europe and across the Atlantic with the United States. It also underlines Europe’s trilemmas in navigating the great power dynamic between the US, Russia and China.
Prerequisites:
— What is the strategy of de-risking?
— What is the NATO?
— What is the European Free Trade Association (EFTA)?
Key takeaways:
— “Xi’s travel to Europe after five years amid a spying scandal points… European investigation into the Chinese dumping of electric vehicles and the prospect of major sanctions against China’s EV makers.”
— “Europe’s response to its geopolitical trilemma will have major consequences for India’s relations with the US, Russia, and China. Europe sees Russia as the principal threat and China as an opportunity and is under pressure from the US to share a greater part of the defence burden in Europe against Russia and contribute to Asian security by boosting the US balancing effort against China.”
— “For Delhi, Beijing is the principal challenge and Moscow is part of the answer. Meanwhile, US domestic politics has become a variable in shaping great power relations.”
— “If Delhi does not want to be a passive victim of potential big shifts in the relations between Washington, Brussels, Moscow, and Beijing, it will need to step up its engagement with Europe. This must include a greater focus on trade and security challenges like Ukraine.”
— “The last few years have seen India end its traditional neglect of Europe. It has enhanced the outreach to individual European powers like France, sub-regional groups like the Nordics, small economic groups like EFTA, and the European Union.”
For Your Information:
— From Explained: China’s trade issues with the European Union (EU) arise mainly out of friction over exports of cheap Chinese electric vehicles (EVs), and constrained access for European companies to markets in China.
— China-made EVs are projected to make up more than a quarter of all EV sales in Europe in 2024, with the country’s share in the market increasing by more than 5 percentage points from a year earlier.
Points to Ponder:
— Significance of Europe for India
— Is the growing dependence of Europe on China, is a cause of concern for India?
— Evolving relationship between India and Europe
Post Read Question:
How does China’s growing dominance in the electric vehicle supply chain pose a challenge for India? What steps should be taken by India to counter it?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Why electric vehicles are at the heart of trade frictions between China and Europe
Explained
Will higher default limit for pesticides in spices impact health?
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national importance.
Mains Examination: GS-II: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health.
What’s the ongoing story- The country’s apex food safety regulator, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), has increased the default limit for pesticide residues in spices to 0.1 mg/kg last month, a ten-fold increase over the previous 0.01 mg/kg. This will be applicable only in cases where the Indian regulation does not specifically mention the maximum residue limits (MRL) for a pesticide for the crop.
Prerequisites:
— What is FSSAI?
— What are the legislative frameworks of FSSAI?
Key takeaways:
— The default MRL for other food products remains the same at 0.01 mg/kg.
— Even with increased limits, the pesticide residues remain in trace amounts that are unlikely to harm human health, said one of the scientists on the panel that recommended the measure to FSSAI.
— The limits increased for spices because:
(i) It is difficult to keep the limits below the 0.01 mg/kg limit because of the confounding effect of the large number of phenols present in spices.
(ii) Imports from other countries may contain pesticides that are approved for use in those countries but not in India.
(iii) There could be seepage of a pesticide not approved in spices from other crops where it might be allowed.
— The activists have said that the higher limit may allow for more pesticides affecting our bodies. Experts from the FSSAI have said that the limits were raised only for the tests to detect the compounds effectively. Action will still be taken if pesticides higher than the limit are used. The government maintains that the limits set by India continue to be the lowest in the world.
Points to Ponder:
— What are the challenges associated with the food safety in India?
— What are some of the important initiatives for food safety in India?
— What are the concerns related to the increasing pesticide limit in spices? How it can impact health?
— What is ethylene oxide?
— What are the global food standards?
Post Read Question:
Prelims
Consider the following statements about the State Food Safety Index (SFSI):
1. The index is released by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to measure the performance of States/UTs on various parameters of Food Safety.
2. The index is released bi-annually.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? given below –
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Mains
What should be the role of different stakeholders in food safety?
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
From MDH to Ceralac and Cadbury – where is the regulator?
Economy
ECI’s letter on deepfakes: What poll panel has said, and what remains unclear
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Indian polity and Governance- Constitution, Political System.
Mains Examination: GS-II: Governance, Constitution, Polity, Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act.
What’s the ongoing story- In its first formal response to the use of deepfakes in this election season, the Election Commission of India (ECI) has directed political parties to not share such content on social media and, if they come to know of such content, to take it down within three hours, and “warn” the person in the party who had shared it.
Prerequisites:
— What is deepfake?
— What is the Model Code of Conduct (MCC)? What are the key provisions of the MCC?
— Read about the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 and Representation of the People Act (RPA), 1951.
Key takeaways:
— The ECI has not discouraged parties from using AI to create campaign material, but has only asked them to refrain from sharing content which is “misinformation or information which is patently false, untrue or misleading in nature and those that impersonate another person”.
—Flagging Erosion of Trust: The ECI said the use of “manipulated, distorted, edited content on social media platforms has the potential to wrongfully sway voter opinions, deepen societal divisions, and erode trust in electioneering process…”.
— Protection of Women: The ECI asked parties to not post or promote content that was derogatory to women or “repugnant to the honour and dignity of women”.
— Reporting of Fakes: Parties have been asked to report unlawful information and fake user accounts that look like their official handles on social media platforms.
— Grievance Committee: In case of “continued presence of such unlawful information or fake user account after reporting to social media platform”, parties have been asked to approach the Grievance Appellate Committee (GAC) under Rule 3A of the IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021.
— Three-hour Deadline: The ECI has directed that “whenever such deepfake audios/ videos come to the notice of political parties, they shall immediately take down the post but maximum within a period of 3 hours and also identify and warn the responsible person within the party”.
Points to Ponder:
— How do new emerging technologies, such as AI and deepfake, pose a challenge to fair and free elections? What is the way forward?
— What is the Centre’s advisory to social media platforms over deepfakes?
— What are the issues associated with the MCC?
— What is the significance of MCC for ensuring free and fair elections?
Post Read Question:
Prelims
With reference to deepfakes, consider the following statements:
1. Deepfakes directly violate the fundamental right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution.
2. It is called deepfakes because they use deep learning technology, a branch of machine learning that applies neural net simulation to massive data sets, to create fake content.
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 Nor 2
Mains
Discuss the role of the Election Commission of India in the light of the evolution of the Model Code of Conduct. (2022)
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
UPSC Essentials | One word a day — Deepfakes
Explained: Model Code of Conduct comes into effect; here’s what that means
Australian parliamentary report questions deal over concerns of ‘child labour’ in India
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Economic and Social Development
Mains Examination: GS-III: Economic development
What’s the ongoing story- At a time when India and Australia are in the middle of negotiations for a broadbasing a mini trade deal into a more comprehensive pact, an Australian parliamentary committee in its report submitted to its lawmakers has raised concerns over child labour in India.
Prerequisites:
— Who is defined as a ‘child’ in India?
— What is the Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA)?
— What is the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)?
— What is the India-Australia Trade deal?
Key takeaways:
— The report stated that the India-Australia trade deal could lead to an increase in goods imports with lower environmental and labour standards.
— The two countries are currently in negotiations for a comprehensive trade deal, the Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA), eliminating of duties on 96 per cent of value of Indian exports to Australia.
— . India’s total exports to Australia in FY24 stood close to $8 billion, 15 per cent higher compared to the previous financial year.
— Referring to Australia-India Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (A-IECTA), the report said, “India has a well-documented presence of child and (forced) labour, making significant contributions to the population of the world in modern slavery”.
— In 2022, the Centre for WTO Studies had argued that the immediate imposition of international labour standards would lead to reduction in the total economic welfare worldwide in developing nations as well as developed nations.
— According to 2011 census, India is home to about 1.01 crore working children between the age of five and fourteen years. As per an Indian parliamentary standing committee report, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, employ over half of India’s child labour.
— According to the standing committee on labour, textiles and skill development, “child workers might have actually increased in urban areas across all sectors and age categories due to the economic woes brought about by the Covid-19 induced crises.”
For Your Information:
— According to the 52nd report of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Labour Textiles And Skill Development Committee, there is an ambiguity in the definition of child under various legislations.
— It stated, “The implementation of the Policy has to go a long way for achieving the objective of elimination of child labour as per commitments made by the county after the ratification of ILO conventions and to achieve the target stipulated in Sustainable Development Goal 8.7 to end all forms of child labour by 2025.”
Points to Ponder:
— What are the causes of child labour in India?
— What are the initiatives taken by the government to curb child labour?
— Role of the International Labour Organisation (ILO)
— What India can do to address the issues posed by the Australian parliamentary report?
Post Read Question:
Examine the reasons behind child labour’s prevalence in India and evaluate the effectiveness of existing institutional measures aimed at protecting children from exploitation.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
The World
Hamas attack, Gaza war, undocumented migration entries top Pulitzer honours
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: GS-II: International Relations,
What’s the ongoing story- The New York Times and The Washington Post were awarded three Pulitzer Prizes apiece on Monday for work in 2023 that dealt with everything from the war in Gaza to gun violence, and The Associated Press won in the feature photography category for coverage of global migration to the U.S.
Prerequisites:
— What is the Pulitzer Prize?
— When were the Pulitzer awards instituted?
— What was the Hamas’ October 7 attack on Israel?
Key takeaways:
— The Pulitzers honored the best in journalism from 2023 in 15 categories, as well as eight arts categories focused on books, music and theater. The public service winner receives a gold medal. All other winners receive $15,000.
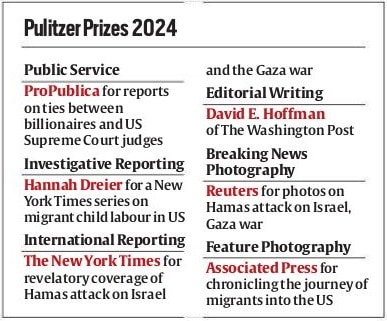
— The awards are administered by Columbia University in New York, which itself has been in the news for student demonstrations against the war in Gaza. The Pulitzer board met away from Columbia this past weekend to deliberate on its winners.
— The prizes were established in the will of newspaper publisher Joseph Pulitzer and first awarded in 1917.
Points to Ponder:
— Who are the Indians who have won the Pulitzer?
— Who was Joseph Pulitzer, after whom the awards are named?
— What are the changes that have been made to the awards?
Post Read Question:
Who was the first Indian to win the Pulitzer Prize?
(a) Gobind Behari Lal
(b) Geeta Anand
(c) Sanghamitra Kalita
(d) Jhumpa Lahiri
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Explained: A history of the Pulitzer Prize; and the Indians who have won it
Express Network
CSIR tells its staff to refrain from wearing ironed clothes on Monday
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: General issues on Environmental Ecology, Biodiversity and Climate Change
Mains Examination: GS-III: Environment
What’s the ongoing story- In an unconventional step to prevent some carbon emissions, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which runs a network of 37 laboratories, has asked its staff, research scholars, and students to “refrain from wearing ironed clothes every Monday starting May 6.”
Prerequisites:
— What is the Swachchata Pakhwada?
— What is the Mission LiFE?
— What is the climate change?
Key takeaways:
— “An iron takes about 800 – 1200 Watts of power to operate, which is 20-30 times more than the power taken by a bulb. 74 per cent electricity in India is produced using coal. Ironing one pair of clothes for a family of five (using an iron for 30-60 minutes) can thus result in the emission of one kg of carbon dioxide.”
— Mumbai-based Energy Swaraj Foundation had launched ‘Wrinkles Achche Hai’ earlier this month. The Foundation believes in Mission LiFE, that is Lifestyle for Environment, a mass movement by India showcasing the country’s dedicated efforts and simple acts in daily lives with ‘significant’ potential to contribute towards fighting climate change.
— CSIR was founded by noted scientist Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar in 1942 to bring industry and scientific institutions to work in tandem in the country.
For Your Information:
— As the world’s third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases, India is a crucial player in the global fight against climate change.
— Under the global climate change framework, countries are supposed to measure their annual greenhouse gas emissions every few years, and submit it to UNFCCC for maintaining a global inventory. This used to be called National Communication, NATCOMs, under the 1997 Kyoto Protocol mechanism. Under the Paris Agreement that has replaced Kyoto Protocol, this submission is called Biennial Update Reports, or BURs.
Points to Ponder:
— What is climate financing?
— What are the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC)?
— What are the initiatives taken by India?
(Thought Process: Read about India’s initiatives- International Solar Alliance (ISA), LiFE, Coalition of Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI), India’s NDA commitment– Points put by India in COP 28)
Post Read Question:
“Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction Pledges of different countries is a: (2022)
(a) Database created by coalition of research organisations
(b) Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
(c) Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
(d) Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
COP28 begins today: India’s role at the climate conferences over the years, key promises, red lines
Here’s how we can save the planet and keep the economy growing
UPSC Ethics and Essay Snippet
‘Wordly Wise’ from The Editorial Page
In the eyes of those who anxiously seek perfection, a work is never truly completed… But abandoned.
-Paul Valery
(Thought Process: What is your understanding of ‘perfection’ and do you believe it is subjective or objective? Can dissatisfaction be considered an important attribute for creating incredible art or creative objects in particular or life goals in general? If the great artists were given the chance to review their own art, do you think they would still point out areas for improvement? Does the pursuit of perfection become a hurdle for you in starting a new project? Can the concept of perfection be applied to the lives of ordinary people?)
May 20: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05







































